Tonsillities
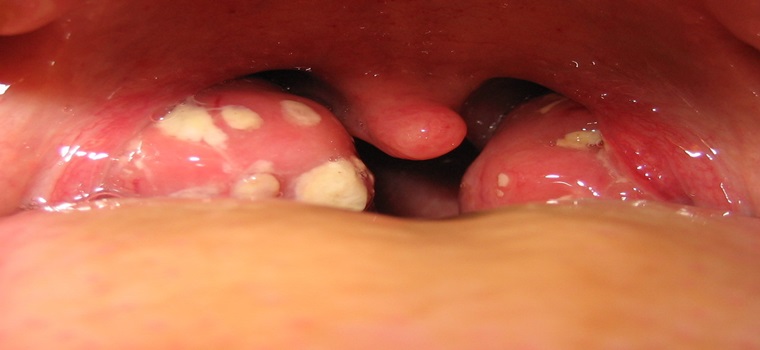
Tonsillitis is inflammation of the tonsils, typically of rapid onset. It is a type of pharyngitis.Symptoms may include sore throat, fever, enlargement of the tonsils, trouble swallowing, and large lymph nodes around the neck. Complications include peritonsillar abscess. Tonsillitis is most commonly caused by a viral infection, with about 5% to 40% of cases caused by a bacterial infection. When caused by the bacterium group A streptococcus, it is referred to as strep throat.Rarely bacteria such as Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Corynebacterium diphtheriae, or Haemophilus influenzae may be the cause.Typically the infection is spread between people through the air.
Throat Pain
Pharyngitis is inflammation of the back of the throat, known as the pharynx.It typically results in a sore throat and fever.Other symptoms may include a runny nose, cough, headache, a hoarse voice. Symptoms usually last three to five days. Complications can include sinusitis and acute otitis media. Pharyngitis is typically a type of respiratory tract infection. Most cases are caused by a viral infection. Strep throat is the cause in about 25% of children and 10% of adults.Uncommon causes include other bacteria such as gonorrhea, fungus, irritants such as smoke, allergies, and gastroesophageal reflux disease. Specific testing is not recommended in people who have clear symptoms of a viral infection such as a cold.

Snoring
Snoring is the vibration of respiratory structures and the resulting sound due to obstructed air movement during breathing while sleeping. In some cases, the sound may be soft, but in most cases, it can be loud and unpleasant. Snoring during sleep may be a sign, or first alarm, of obstructive sleep apnea (OSA). Research suggests that snoring is one of the factors of sleep deprivation.

Voice Change
A voice change or voice mutation, sometimes referred to as a voice break, commonly refers to the deepening of the voice of people as they reach puberty. Before puberty, boys and girls have roughly similar vocal pitch, but during puberty the male voice typically deepens an octave, while the female voice usually only deepens by a few notes. A similar effect is a voice crack during which a person's voice suddenly and unintentionally enters a higher register (usually falsetto) for a brief period of time. This may be caused by singing or talking at a pitch outside the person's natural vocal range, stress, emotional tension, or the physical changes associated with puberty. An instance of a voice crack (when associated with puberty) lasts for only a moment and generally occurs less frequently as a person grows into maturity.
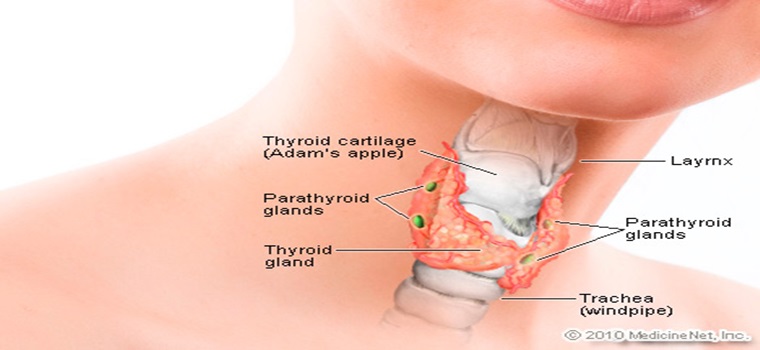
Thyroid
The thyroid gland, or simply the thyroid /ˈθaɪrɔɪd/, is an endocrine gland in the neck, consisting of two lobes connected by an isthmus. It is found at the front of the neck, below the Adam's apple. The thyroid gland secretes thyroid hormones, which primarily influence the metabolic rate and protein synthesis. The hormones also have many other effects including those on development. The thyroid hormones triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4) are created from iodine and tyrosine. The thyroid also produces the hormone calcitonin, which plays a role in calcium homeostasis.

Smell Problem
Smell Problem is the inability to perceive odor or a lack of functioning olfaction—the loss of the sense of smell. Anosmia may be temporary, but some anosmia (including traumatic anosmia) can be permanent. Anosmia is due to a number of factors, including an inflammation of the nasal mucosa, blockage of nasal passages or a destruction of one temporal lobe. Inflammation is due to chronic mucosa changes in the paranasal sinus lining and the middle and superior turbinates.